The evolution of game consoles has been a fascinating journey, marked by innovation, competition, and a relentless pursuit of immersive gaming experiences. From the simplistic designs of the early 1970s to the complex systems of today, gaming consoles have undergone significant transformations. This article provides a retrospective look at the history of game consoles, tracing their development from the Atari to the latest next-gen systems.
The Birth of Home Consoles: The 1970s
The journey of home gaming consoles began in the early 1970s. In 1972, the Magnavox Odyssey was released as the first commercial home video game console. It featured simple graphics and a handful of built-in games, primarily consisting of Pong clones and other rudimentary titles. Players used plastic overlays for the screen to add some visual elements to the otherwise monochrome display. Although it was not a commercial success, the Odyssey laid the groundwork for future home gaming.
Atari’s Breakthrough: The Late 1970s
In 1977, Atari launched the Atari 2600, which revolutionized the gaming landscape. It was one of the first consoles to use interchangeable cartridges, allowing players to purchase and play multiple games on a single device. The Atari 2600’s success was propelled by iconic titles like “Space Invaders,” “Pitfall!,” and “Adventure.” This console became a cultural phenomenon, paving the way for the gaming industry as we know it today.
However, the video game market experienced its first crash in 1983 due to oversaturation and poor-quality games, leading to a significant decline in console sales.
The Rise of Nintendo and Sega: The 1980s

The mid-1980s marked a renaissance for the gaming industry, primarily driven by Nintendo and Sega. In 1983, Nintendo released the Famicom (Family Computer) in Japan, which was later rebranded as the Nintendo Entertainment System (NES) when it launched in North America in 1985. The NES revitalized the market with its innovative design, quality games, and a rigorous licensing system that ensured game quality.
The Console Wars: Nintendo vs. Sega
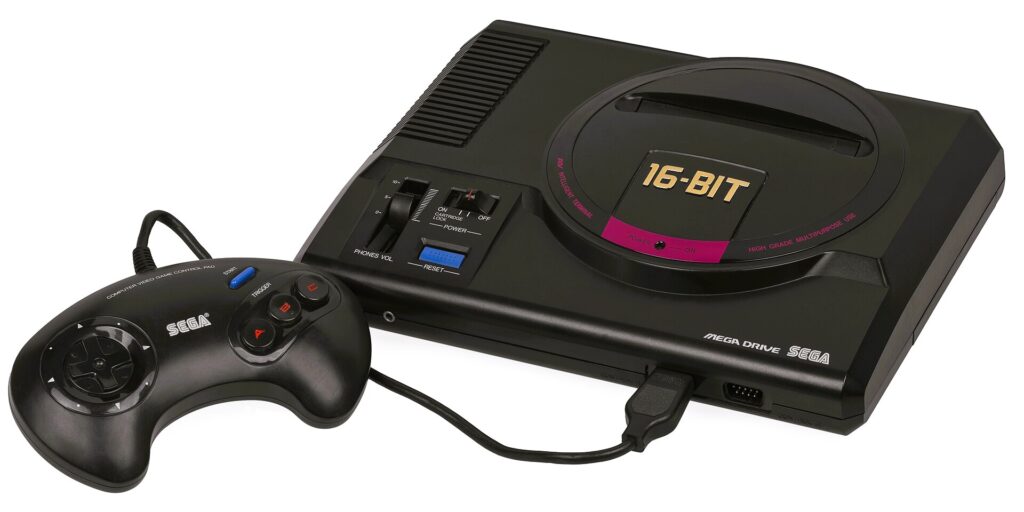
In 1989, Sega released the Genesis (known as the Mega Drive outside North America), which introduced 16-bit graphics and a more mature gaming library. This marked the beginning of the “console wars,” as Nintendo and Sega competed fiercely for market dominance. The Genesis boasted popular titles like “Sonic the Hedgehog,” appealing to a slightly older demographic.
Nintendo responded with the Super Nintendo Entertainment System (SNES) in 1990, which featured advanced graphics, improved sound capabilities, and classic titles such as “Super Mario World” and “The Legend of Zelda: A Link to the Past.” The competition between Nintendo and Sega laid the foundation for many gaming franchises and defined the gaming landscape for years to come.
The Advent of 3D Graphics: The 1990s
The 1990s ushered in a new era of gaming with the introduction of 3D graphics and CD-ROM technology. Sony entered the console market with the PlayStation in 1994, offering a more powerful system with impressive graphics and an extensive library of games. The PlayStation’s success was driven by titles like “Final Fantasy VII” and “Metal Gear Solid,” solidifying Sony’s position in the gaming industry.
The Rise of 3D Graphics
Meanwhile, Nintendo released the Nintendo 64 in 1996, featuring groundbreaking 3D graphics and multiplayer capabilities. Titles such as “Super Mario 64” and “The Legend of Zelda: Ocarina of Time” became benchmarks for game design and storytelling in the 3D era. The shift from 2D to 3D graphics changed the way games were designed and played, enhancing immersion and player engagement.
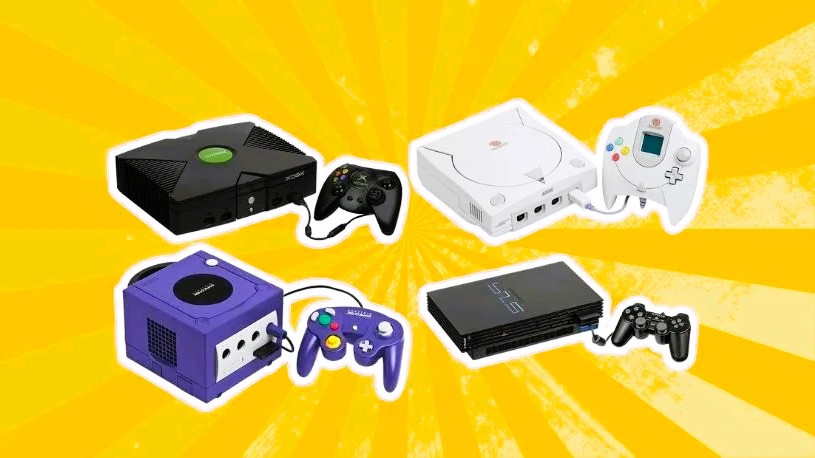
The Sixth Generation: The Early 2000s
The early 2000s saw the emergence of the sixth generation of consoles, including the Sony PlayStation 2, Microsoft Xbox, and Nintendo GameCube. The PlayStation 2, released in 2000, became the best-selling console of all time, with a vast library of games and the added capability of playing DVDs, which contributed to its popularity.
Microsoft’s Entry into the Market
Microsoft entered the gaming console market with the Xbox in 2001, introducing online gaming through Xbox Live. This service allowed players to connect with friends and compete in multiplayer matches, revolutionizing the way people played video games. The Xbox’s success was driven by exclusive titles like “Halo: Combat Evolved,” which became a defining franchise for the brand. Read about how sound improves gaming experience and immersion in this article.
The Seventh Generation: HD Gaming and Online Connectivity
The seventh generation of consoles began in the mid-2000s with the release of the Xbox 360 (2005), PlayStation 3 (2006), and Nintendo Wii (2006). This generation marked a significant leap in graphics quality, with the introduction of high-definition (HD) graphics and online connectivity.
The Impact of Motion Controls
The Nintendo Wii introduced motion controls, allowing players to physically interact with games. This innovative approach attracted a broader audience, including casual gamers and families. Titles like “Wii Sports” and “Super Mario Galaxy” showcased the Wii’s unique capabilities, making it one of the most successful consoles of its time.
Meanwhile, the Xbox 360 and PlayStation 3 competed fiercely, offering advanced online features and a wide array of exclusive titles. The introduction of digital downloads and downloadable content (DLC) changed the way players accessed and experienced games.
The Eighth Generation: The Era of Digital Distribution
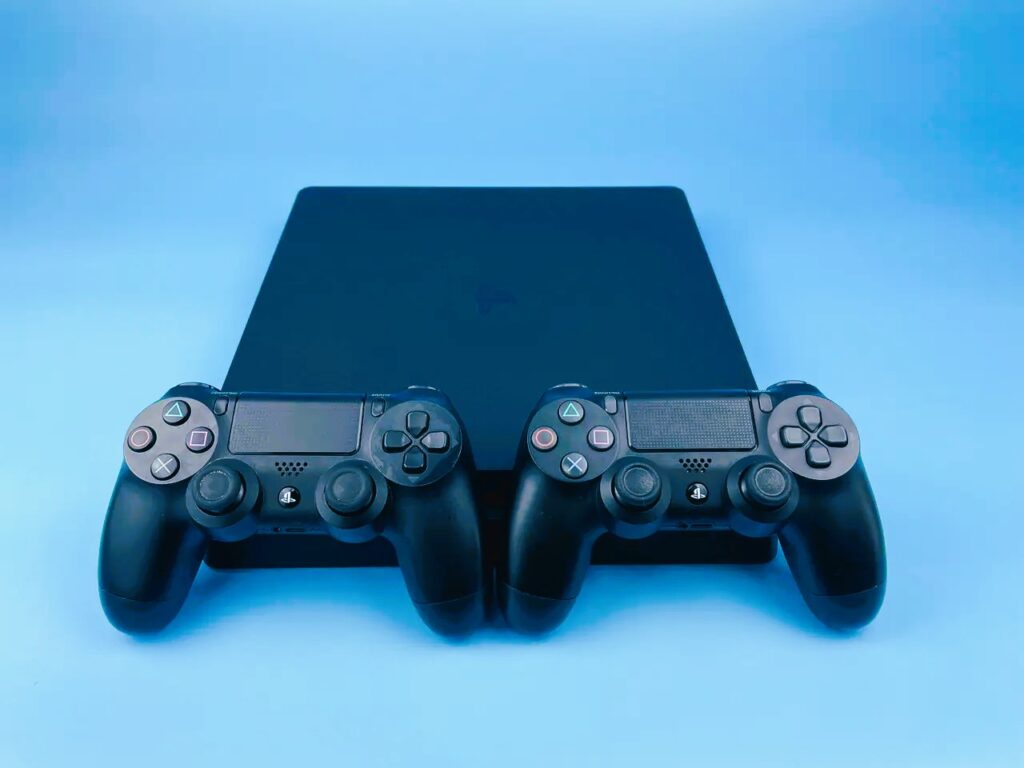

The eighth generation of consoles, which began in 2013, included the Xbox One, PlayStation 4, and Nintendo Switch. This generation further embraced digital distribution, with players increasingly downloading games instead of purchasing physical copies.
The Rise of Streaming and Remote Play
The PlayStation 4 and Xbox One focused heavily on social features and online connectivity, allowing players to share gameplay and stream live content. The Nintendo Switch introduced a hybrid model, combining handheld and console gaming, appealing to both casual and hardcore gamers. With titles like “The Legend of Zelda: Breath of the Wild” and “Super Mario Odyssey,” the Switch quickly became a favorite among gamers.
Next-Gen Consoles: The Future of Gaming
In late 2020, the gaming landscape witnessed the launch of the PlayStation 5 and Xbox Series X/S. These next-gen consoles push the boundaries of graphics, processing power, and storage capacity, utilizing SSDs for faster load times and enhanced performance. With features like ray tracing and 120 FPS gameplay, the future of gaming looks promising.
Cloud Gaming and Subscription Services
Looking ahead, cloud gaming is set to reshape the console market. Services like Google Stadia, NVIDIA GeForce NOW, and Xbox Cloud Gaming offer gamers the ability to stream high-quality games without needing powerful hardware. Subscription models, such as Xbox Game Pass and PlayStation Plus, provide players with access to extensive libraries of games for a monthly fee, changing the way games are consumed.
The history of game consoles is a testament to the ingenuity and creativity of the gaming industry. From the humble beginnings of the Magnavox Odyssey to the advanced technologies of today’s consoles, gaming has evolved dramatically over the decades. As we look to the future, the potential for further innovation remains limitless. For more insights into gaming history and technology, visit Wikipedia for the latest updates and developments in the world of gaming.
As technology continues to advance, it will be exciting to see how gaming consoles adapt and evolve to meet the demands of players around the world, ensuring that gaming remains a vibrant and ever-changing form of entertainment.